Dipole Moment
Dipole moment is possible between charges which are separated by a distance, d. Dipole moment is measure of polarity of a molecule. Dipole moment depends on two factors (i) magnitude of charge (ii)distance between charges. Dipole moment is a vector quantity.
In a covalent bond one of the atom is relatively more electronegative than other atom. Therefore, shared electron pair is close to more electronegative atom and cause partial negative charge on more electronegative atom and partial positive charge on less electronegative atom.
❉ Dipole moment (𝜇) = |e| x d, where |e| = magnitude of charge and d = bond length.
❉ dipole moment of a covalent bond is represented by ⇸, arrow pointing towards more electronegative atom and vertical line on the arrow point towards less electronegative atom.
❉ Units of dipole moment is Debye and 1D = 3.33 x 10−30 Cm , 1D = 10−18 e.s.u-cm.
❉ Dipole moment is a vector quantity and geometry of covalent molecule is needed to calculate dipole moment of covalent molecule.
❉ Applications of dipole moment:
(i) To check the polarity of molecule
(ii) To calculate percentage of ionic character of covalent bond.
❉ Dipole moment of molecule ﹦ 0 ➡︎ Non – Polar molecule
Dipole moment of molecule ≠ 0 ➡︎ Polar molecule
❉ Percentage of ionic character of covalent bond = (experimental 𝜇/ Theoretical 𝜇) x 100
❉ Dipole moment of homo diatomic molecules (example: O2, H2,N2 etc.,) is zero because there is no charge separation due to the same electronegativity of both the atoms
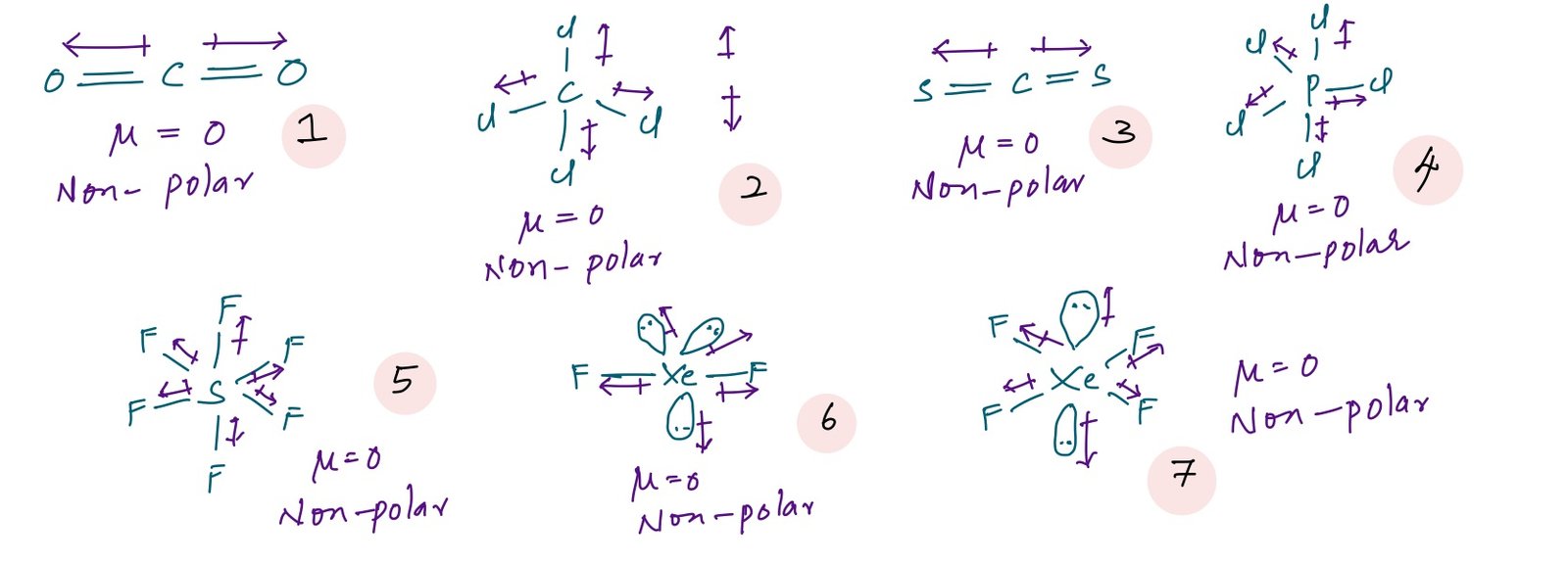
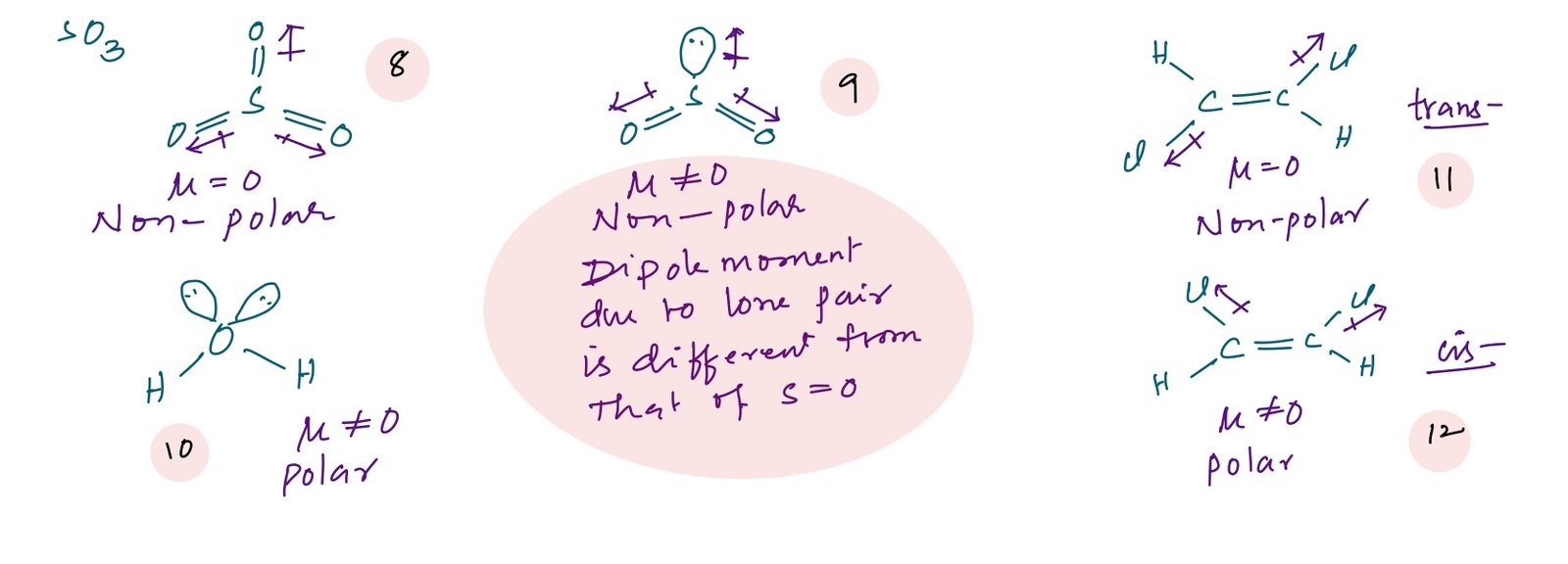
In case of symmetric molecules dipole moment is zero. Example: dipole moment of CO2, CCl4, CH4, SF6, PCl5, XeF2, XeF4, SO3, B2H6 etc., is zero. Dipole moments can be calculated by using vector addition based on the geometry of the molecule.
Compounds 1 to 7 are non-polar molecules because these all are perfect symmetric molecules which gives a net resultant dipole moment as zero.
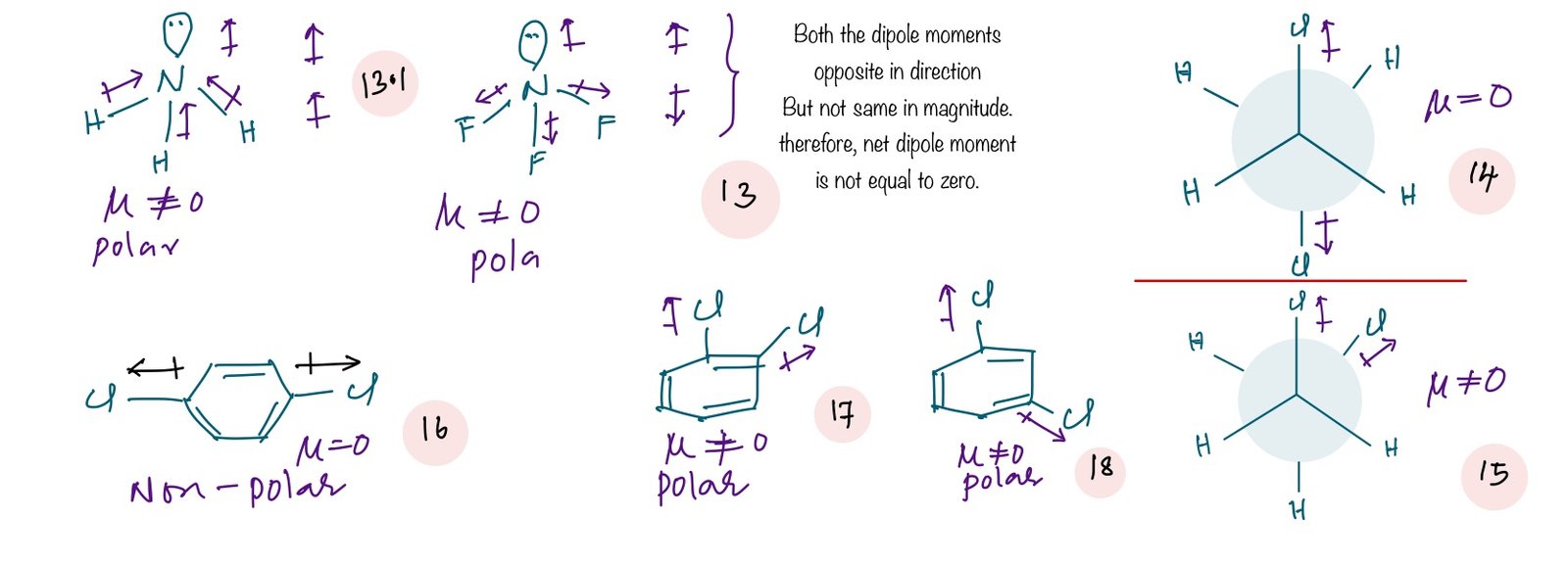
Out of two conformational isomers of 1,2 – dichloro ethane (14 and 15) staggers isomer (14)has a net dipole moment of zero. In case of cis and trans isomers of 1,2-dichloroethene trans isomer net dipole moment is zero because both dipole moments due to C-Cl bonds are same in magnitude and opposite in direction. Dipole moment of NH3(13.1) is more than that of NF3(13) even though fluorine is more electronegative than hydrogen because: In NH3, dipole moment due to lone pair and due to three N-H bonds are in the same direction whereas in NF3 dipole moment due to lone pair and due to the three N-F bonds are in opposite direction.
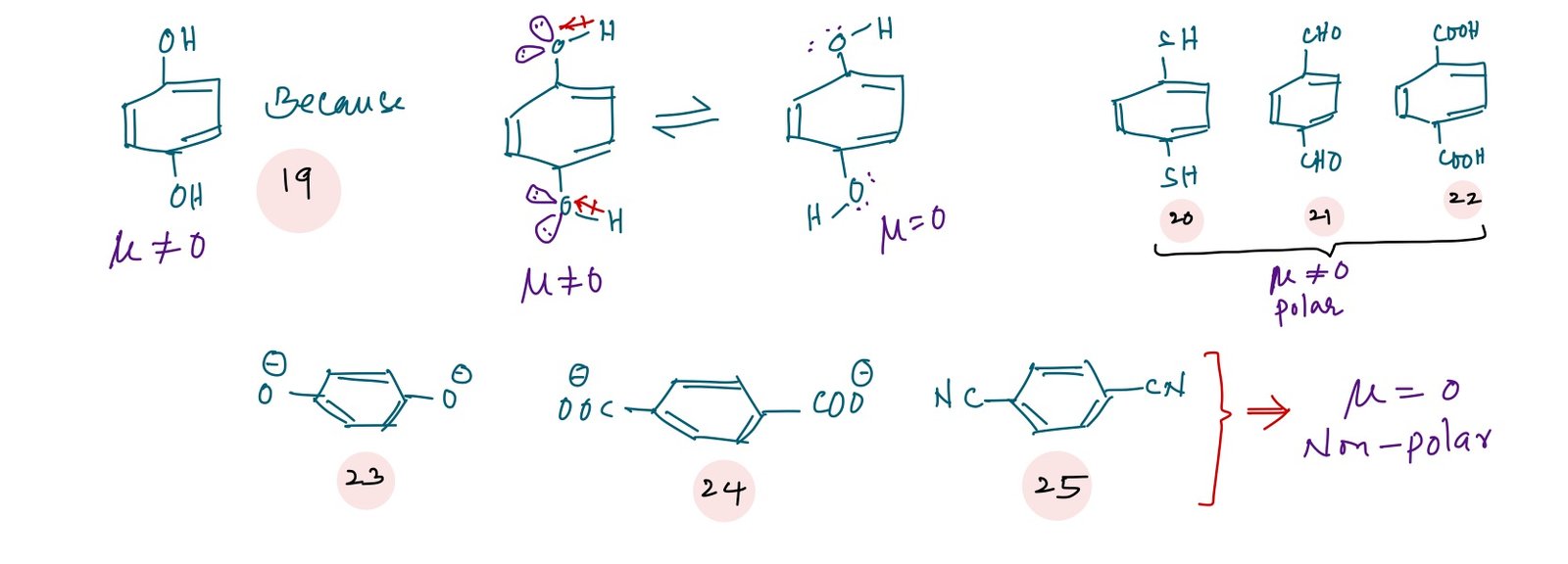
In case of p-dihydroxybenzene(19), benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid(22), terephthalaldehyde(21), dimethyl terephthalate are non – polar because the group (-OH or COOH) are not linear. Therefore, net dipole moment is not equal to zero. In case of compounds (23), (24) and (25) are non-polar due to the linear groups attached at 1,4 positions of benzene which results a net dipole moment is zero.