INTEXT QUESTIONS: HALOALKANES & HALOARENES
Chem Avenue CBSE-12, Organic chemistry #CBSE, #Chemistry, #Class 12, #HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES, #INTEXT QUESTIONS NCERT, #NCERT 0
HALOALKANES & HALOARENES: CBSE INTEXT QUESTIONS
Q 6.1 Write structures of the following compounds:
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
(ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
(iii) 4-tert butyl-3-iodoheptane
(iv) 1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
(v) 1-Bromo-4-sec butyl-2-methylbenzene.
ANSWER: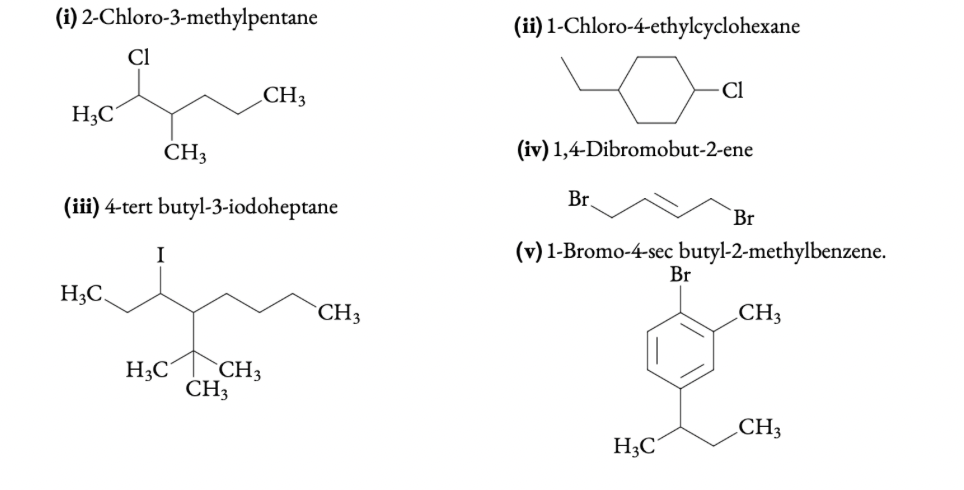
Q 6.2 Why is sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI?
ANSWER:
H2SO4 is strong oxidizing agent and it oxidizes iodide(I−) to I2. Therefore, reaction of ROH with KI + H2SO4 do not form RI(alkyl iodide). Therefore, ROH should be treated with KI+ H3PO4 to prepare RI, because KI + H3PO4 generates HI and HI reacts with ROH to form RI.
Q 6.3 Write structures of different dihalogen derivatives of propane.
ANSWER:
Dihalide can be isolated, geminal dihalide and vicinal dihalide. In geminal dihalide both the halogen atoms attached to the same carbon atom(example: 1 and 4) and in vicinal dihalide two halogen atoms attached to two adjacent carbon atoms (example: 3)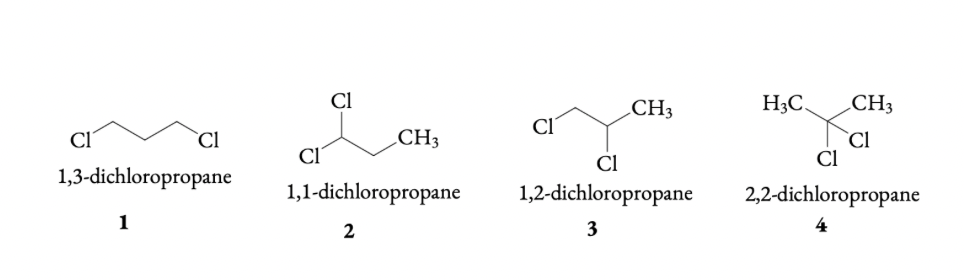
Q 6.4 Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields
(i) A single monochloride.
(ii) Three isomeric monochlorides.
(iii) Four isomeric monochlorides.
ANSWER:
All possible isomers of alkanes with formula are: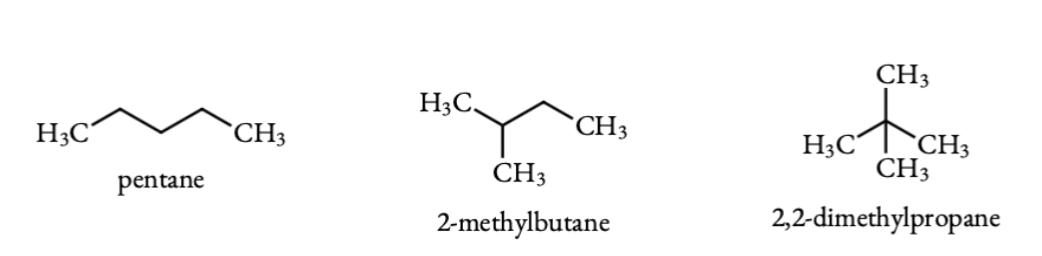
On photo chemical mono chlorination the following products are possible. Substitute hydrogen atom by a chlorine atom gives the possible mono chloroform pentanes.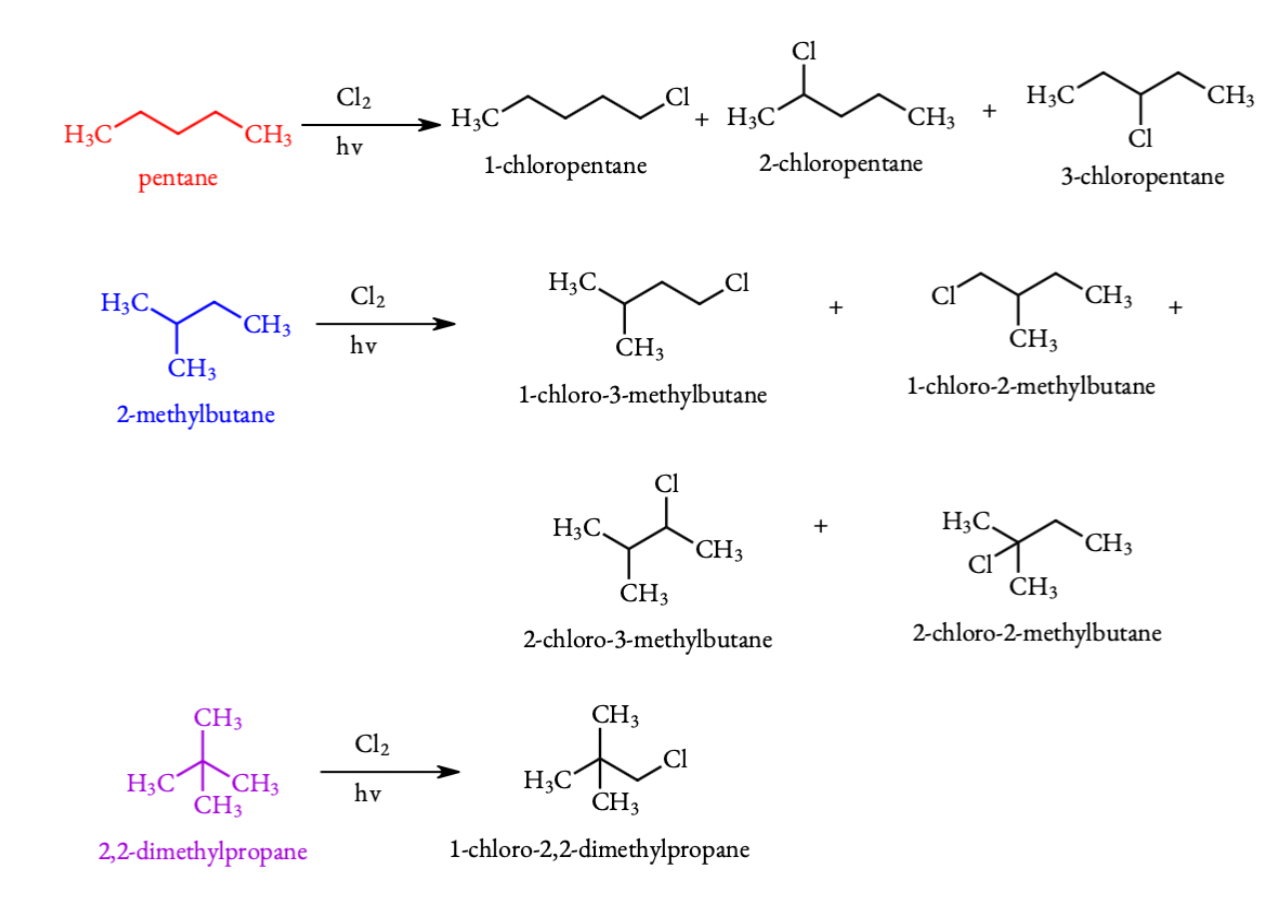
From the above equations it is clear that pentane on chlorination gives three monochloro pentanes, isopentane(2-methyl pentane) gives 4 monochloro pentanes and neopentane(2,2-dimethyl pentane) gives only one monochloro pentane.
(i) neopentane gives a single mono chloride.
(ii)n-pentane gives three monochlorides.
(iii)isopentane gives 4 monochlorides.
Q 6.5 Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: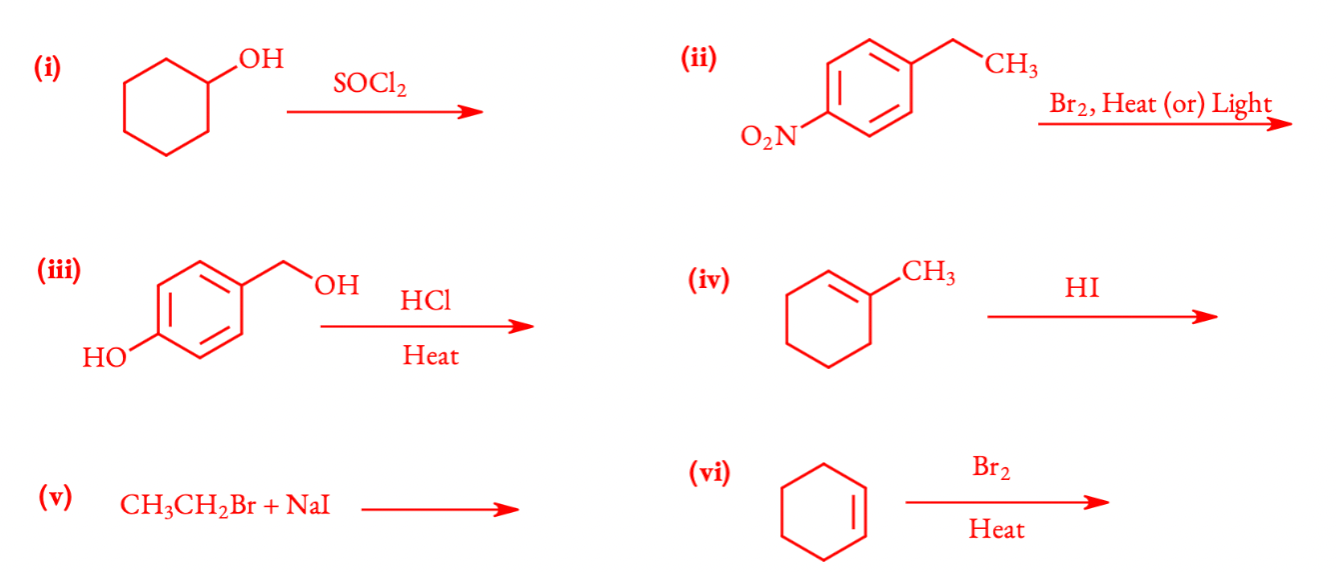
ANSWER:
(i) R − OH + SOCl2 ➞ R − Cl + SO2 + HCl
(ii) Br2/heat or light free radical substitution takes place. Benzylic hydrogen is substituted instead of ring hydrogen substitution. If the reagent is Br2/Fe, ring substitution takes place.
(iii) − OH attached to sp3 carbon is substituted by nucleophile (Cl−) and phenol do not undergo nucleophilic substitution. Therefore, − OH attached to the benzene ring is not replaced by Cl.
(iv) Markovnikov addition of HI to alkene. ‘I’ attached to the double bonded carbon with less number of hydrogens.
(v) Finkelstein reaction is the nucleophilic substitution of R − Cl or R − Br with NaI gives iodoalkane.
(vi) Electrophilic addition of Br2 to alkene forms vicinal dibromide.
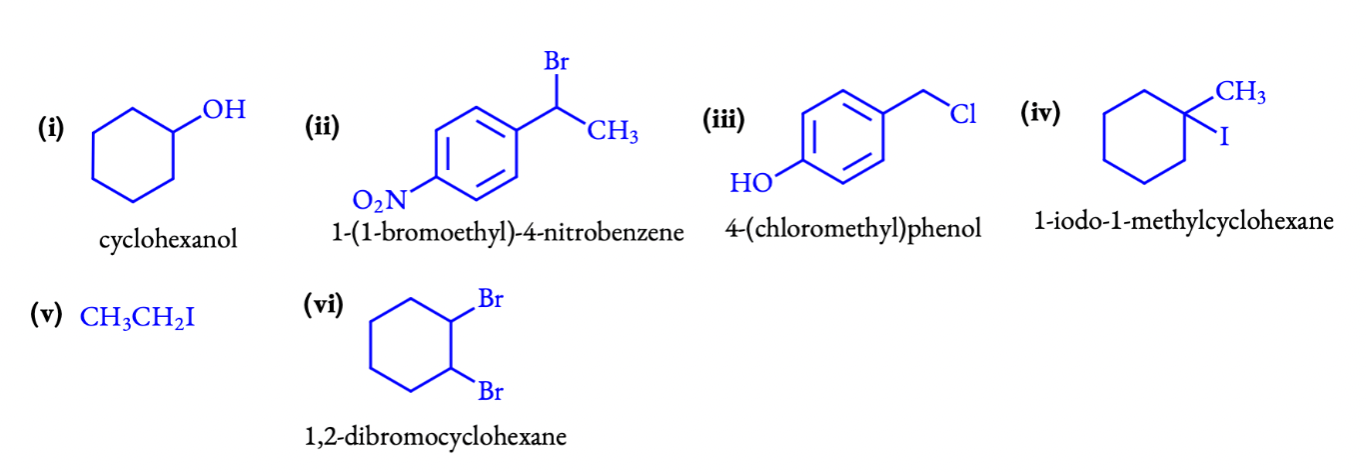
Answers:
(i) cyclohexanol
(ii)1-(1-bromoethyl)-4-nitrobenzene
(iii)4-(chlorophenyl)phenol
(iv)1-iodo-1-methylcyclohexane
(v)iodoethane. (vi) 1,2-dibromocyclohexane
Q 6.6 Arrange each set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points.
(i)Bromomethane, Bromoform, Chloromethane, Dibromomethane.
(ii)1-Chloropropane, Isopropyl chloride, 1-Chlorobutane.
(i) Boiling point is directly proportional to the molecular mass. Therefore, increasing order of boiling point is:
Chloromethane (CH3Cl)<Bromomethane(CH3Br)<dibromomethane(CH2Br2)< bromoform(CHBr3).
(ii) In case of isomeric alkyl halides boiling point decreases as the branching increases. 1 – chlorobutane molecular mass is more than rest of the two and in between 1 – chloropropane and isopropyl chloride, 1 – chloropropane has more boiling point because of no branching.
Boiling point: Isopropyl chloride < 1 – chloropropane < 1 – chlorobutane
Q 6.7 Which alkyl halide from the following pairs would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
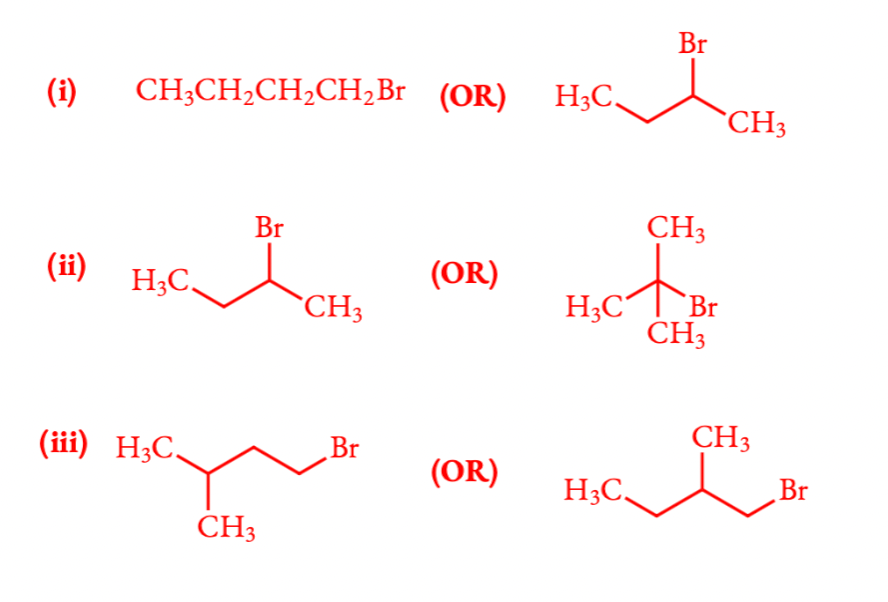
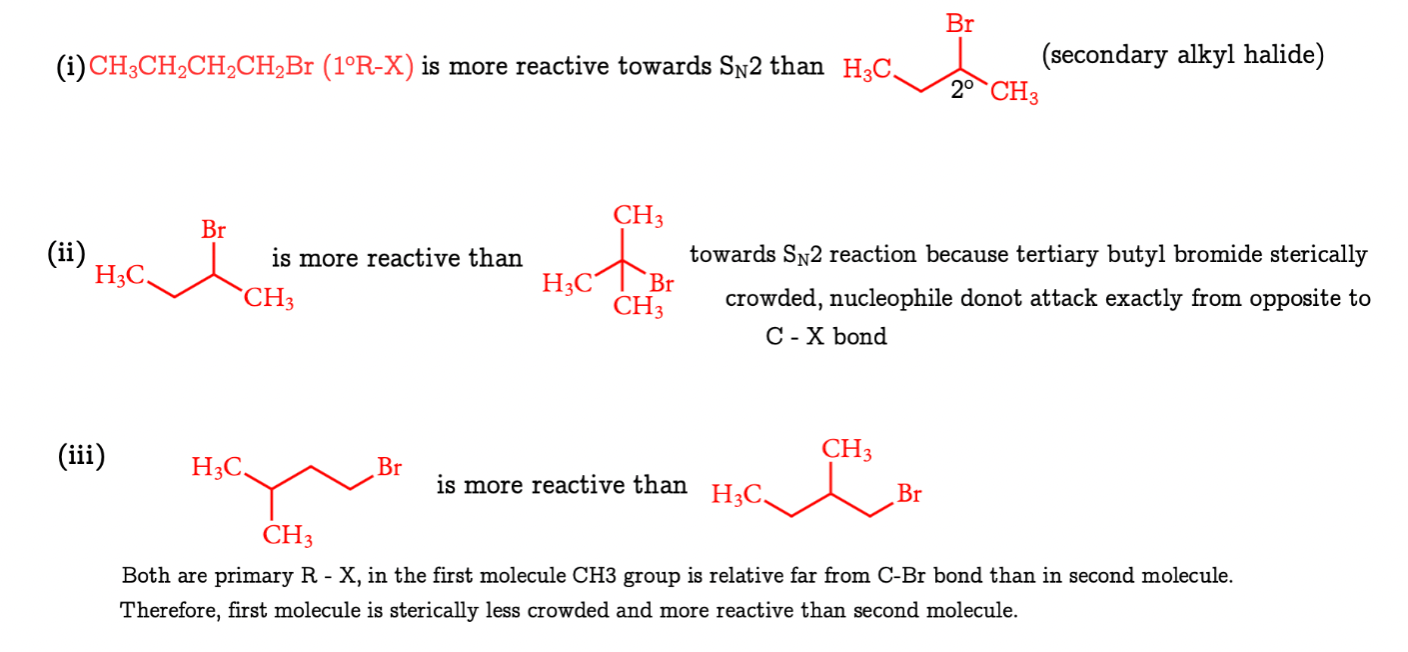
Order of reactivity of SN2 reactions: 1o R − X > 2o R − X > 3o R − X because SN2 reactivity depends on the steric crowding at C − X bond.
Q 6.8 In the following pairs of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes faster SN1 reaction?

Reactivity order of SN1 reaction depends on stability of carbocation formed in the first step(rate determining step). In general reactivity order is: 3o R − X > 2o R − X > 1o R − X. Any alkyl halides which forms relatively stable carbocation proceeds through SN1 mechanism.
(i) Tertiary butyl chloride is more reactive than 3-chlorobutane.
(ii) 2 – chloroheptane is more reactive than 1 – chlorohexane.
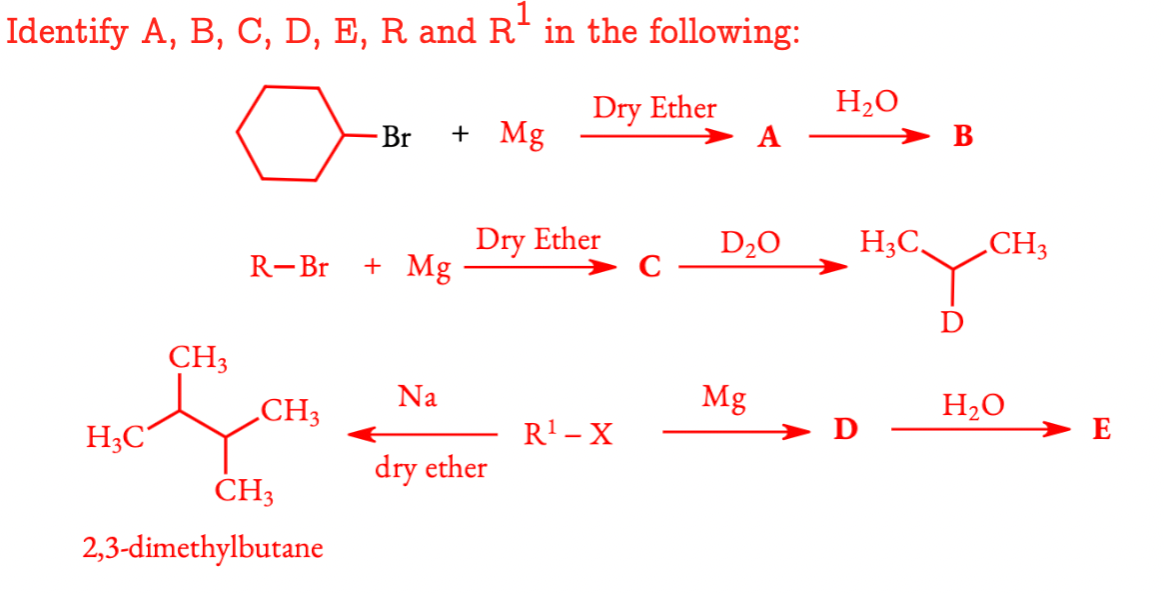
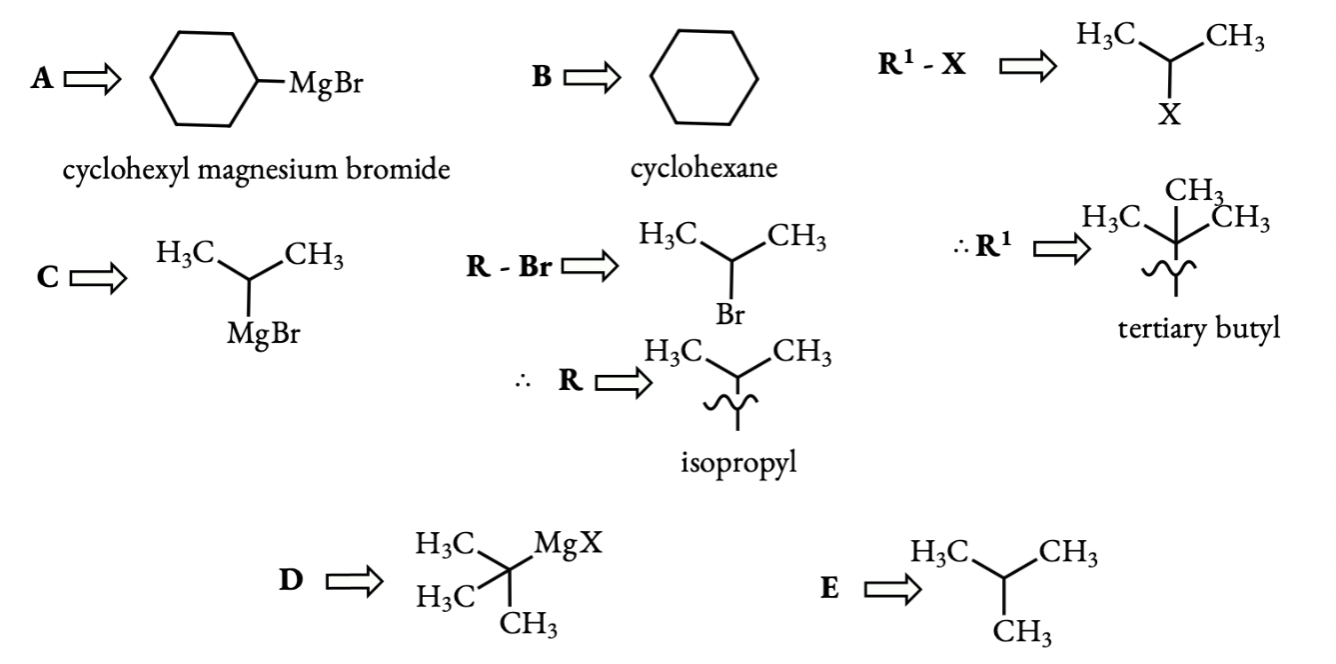
Q 6.9 Identify A, B, C, D, E, R and R1 in the following: