EQUILIBRIUM & EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
Reactions can be reversible and irreversible. Reversible reactions occurs both the directions, reactants to products (Forward reaction) and product to reactant(Backward reaction). Irreversible reactions end-up with products, once reactants convert to products they do not revert back to give reactants again. Equilibrium is possible in reversible reactions, generally in a closed container. Limiting reagent is the reactant which gets consumed first and limiting reagent not applicable for revisable reactions at equilibrium because none of the substances get consumed completely in the process.
Equilibrium is a state at which rates of forward and backward reactions are equal and the measurable quantities like concentration and pressures of reactants and products are constant. In general hypothetical chemical equilibrium represented as follows:
aA + bB ⇋ cC + dD
Equilibrium are of three types: Physical equilibrium, chemical equilibrium and ionic equilibrium. Physical equilibrium involves the equilibrium in physical processes like phase transition (Solid ⇋ Liquid; Liquid ⇋ Gas; Solid ⇋ Gas) and dissolution process of solid and gas in liquid (Solid + Liquid ⇋ Solution; Gas + Liquid ⇋ Solution).Chemical equilibrium is the equilibrium established between molecules and the ionic equilibrium is the equilibrium between dissociated ions and undissociated molecules example:(CH3COOH(aq)⇋CH3COO-(aq) + H+(aq)). Chemical equilibrium are of two categories Homogeneous equilibrium and Heterogeneous equilibrium.
Homogenous equilibrium: In homogeneous equilibrium all the substances in the same physical state. Examples are given below
Heterogeneous equilibrium: In heterogeneous equilibrium all the substances are not in the same physical state. Examples are given below


Rate at equilibrium
At equilibrium rate of forward reaction is same as that of backward reaction.
(Rate)f = (Rate)b
Equilibrium is dynamic in nature
Equilibrium state is dynamic in nature because it proceeds towards forward and backward reactions with equal rates.
Equilibrium concentrations
At equilibrium concentration/pressures of reactants and products are constant and can be calculated through equilibrium constant.
Equilibrium constant (K_c)
Equilibrium constant (K_c) is the ratio of product of concentrations of products raised to the power values as their coefficients to the product of concentrations of reactants raised to the power value of their coefficients in a balanced chemical equilibrium. Equilibrium constant is temperature dependent.
NOTE: In K_c expression consider gaseous and aqueous substances and do not consider solid and liquid substances.

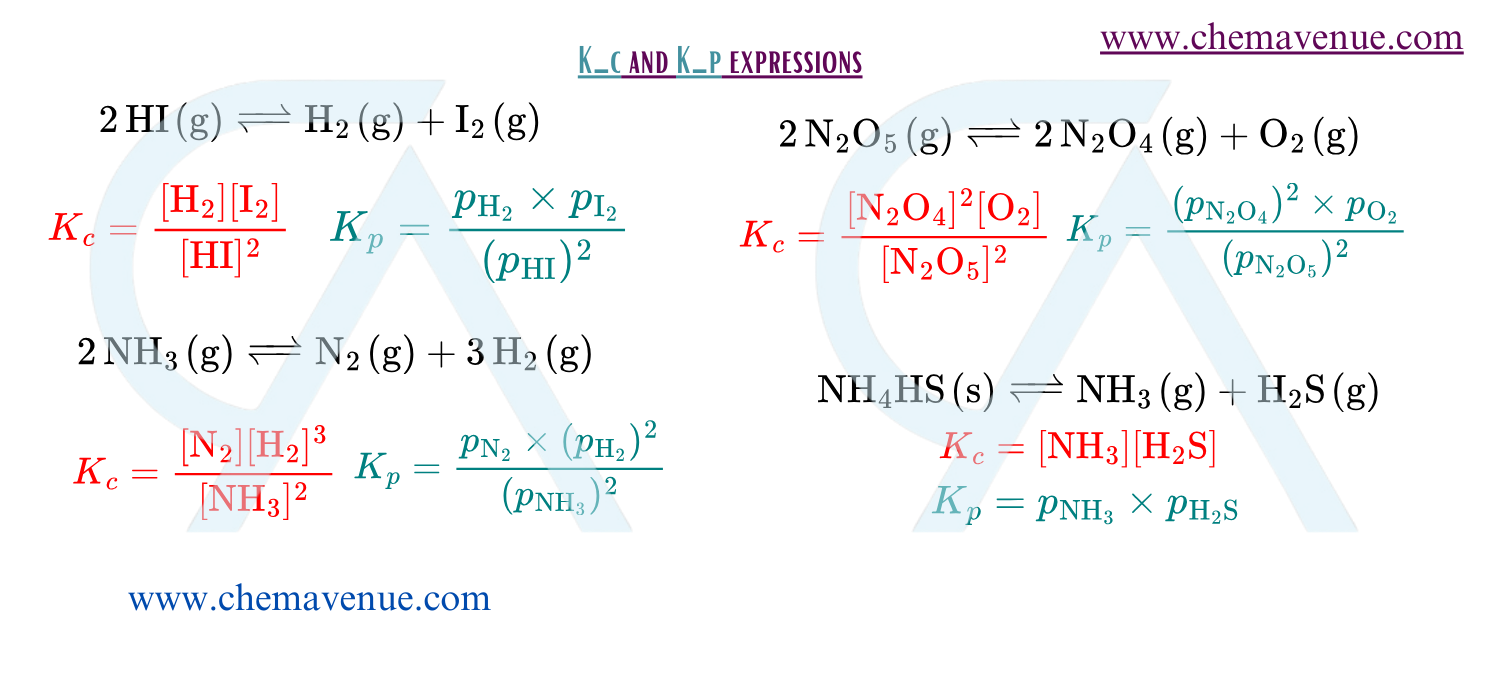
Equilibrium Constant(K_p)
Equilibrium constant (K_c) is the ratio of product of partial pressures of products raised to the power values as their coefficients to the product of partial pressures of reactants raised to the power value of their coefficients in a balanced chemical equilibrium. While writing K_p consider only gaseous components.
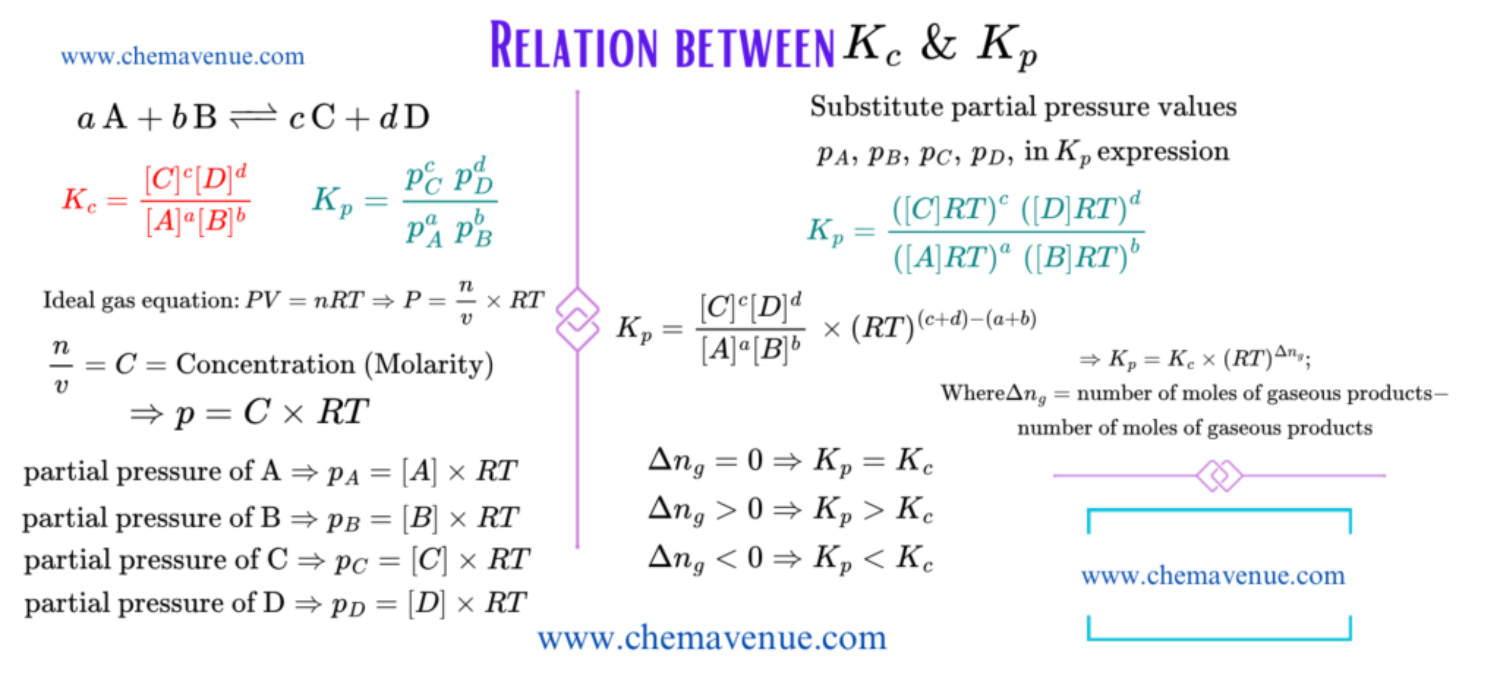
Relation between K_c and K_p
As we know that concentration and pressure related to each other which can be derived from ideal gas equation. Therefore, K_c and K_p are related to each other and it is clear from the given relation.
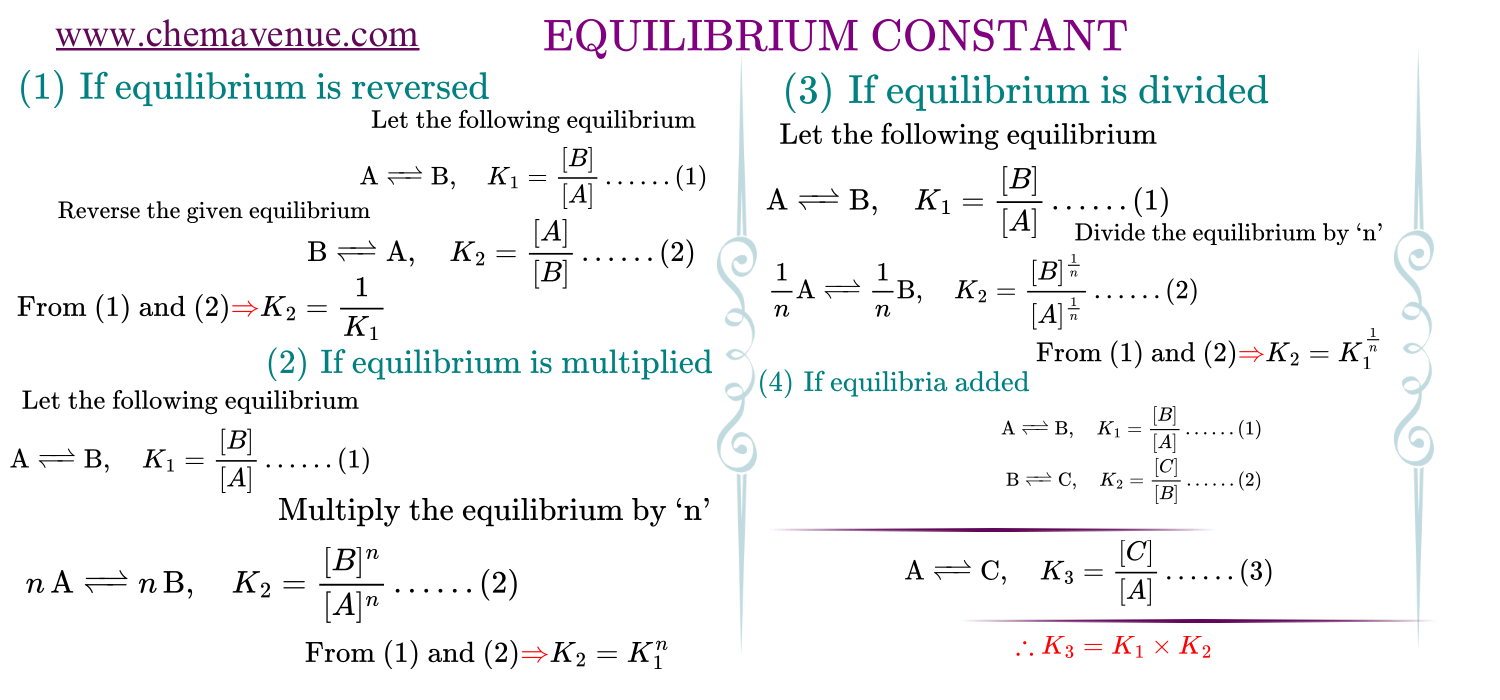
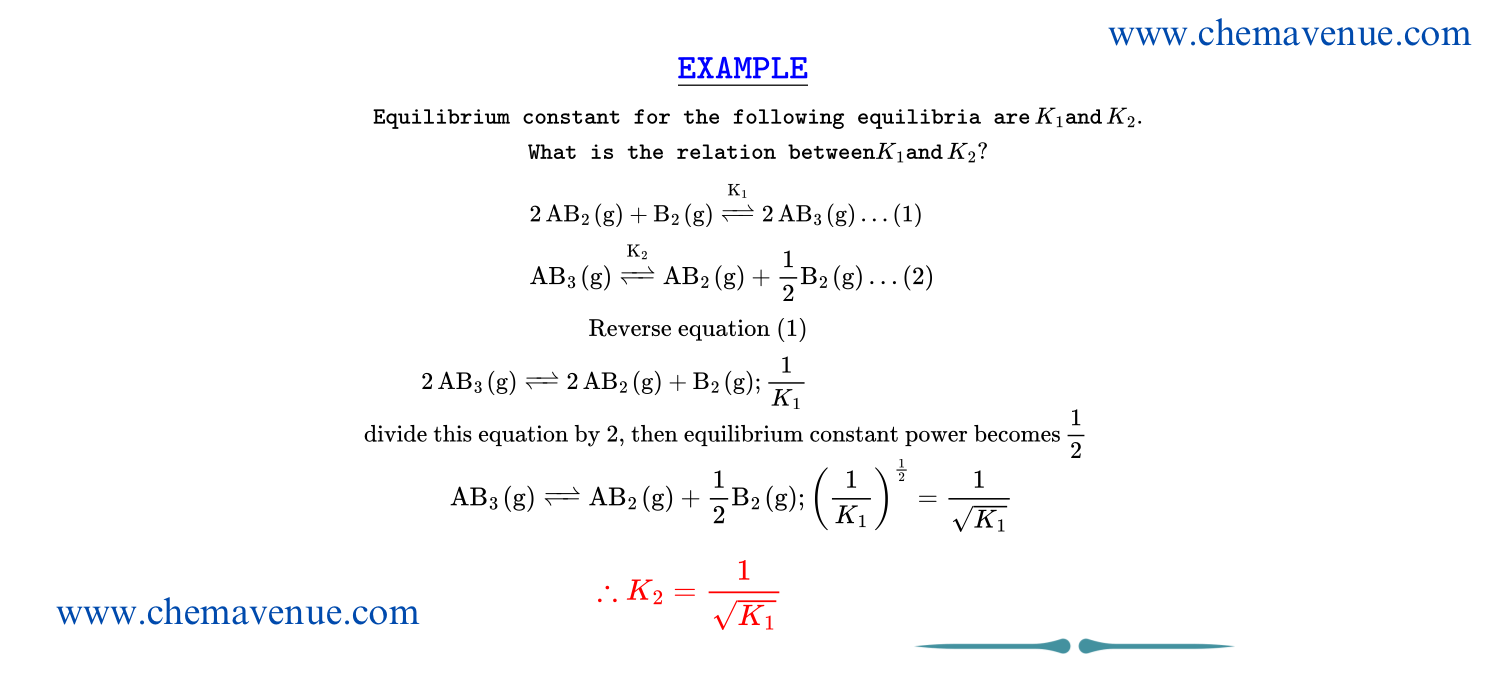
Dependence of K_c with coefficients of equilibria
Equilibrium constant is extensive property there it changes as the equilibrium changes that is it changes as the equilibrium multiplied, divided, reversed.
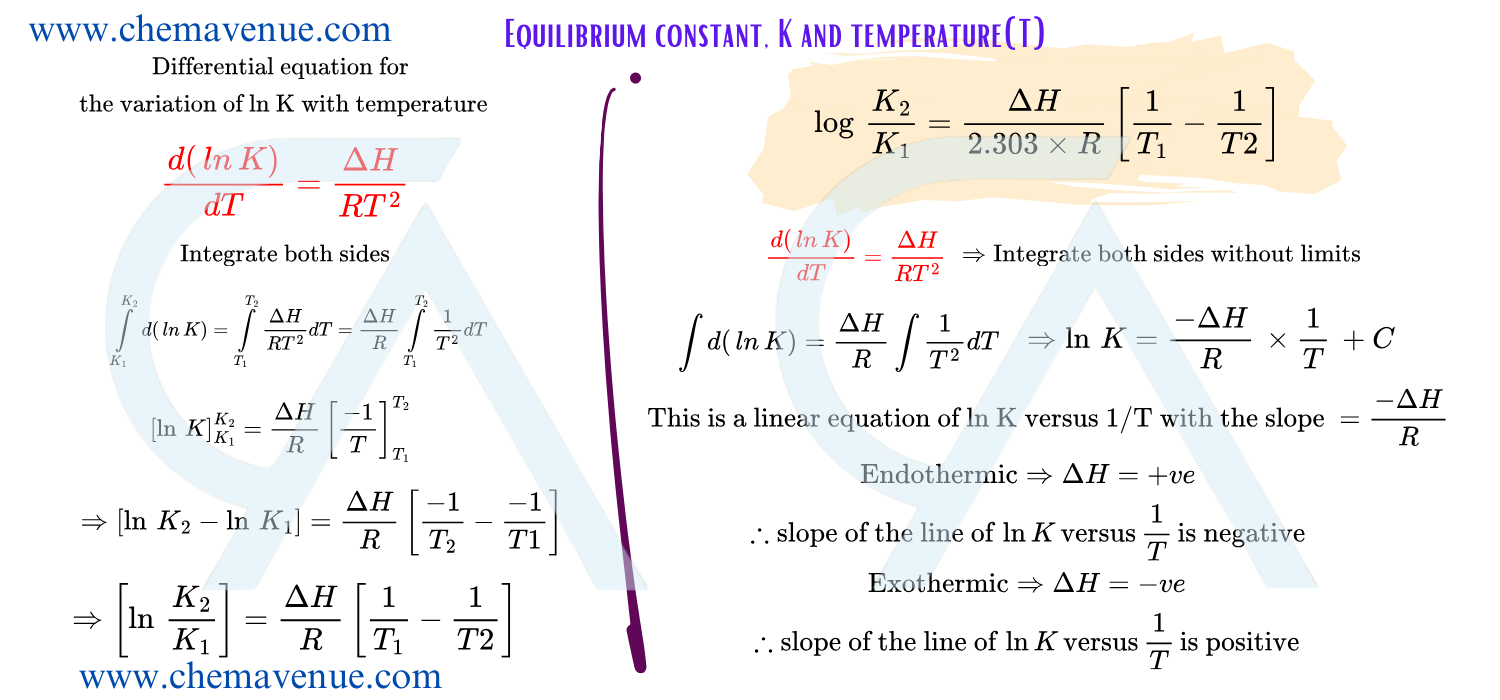
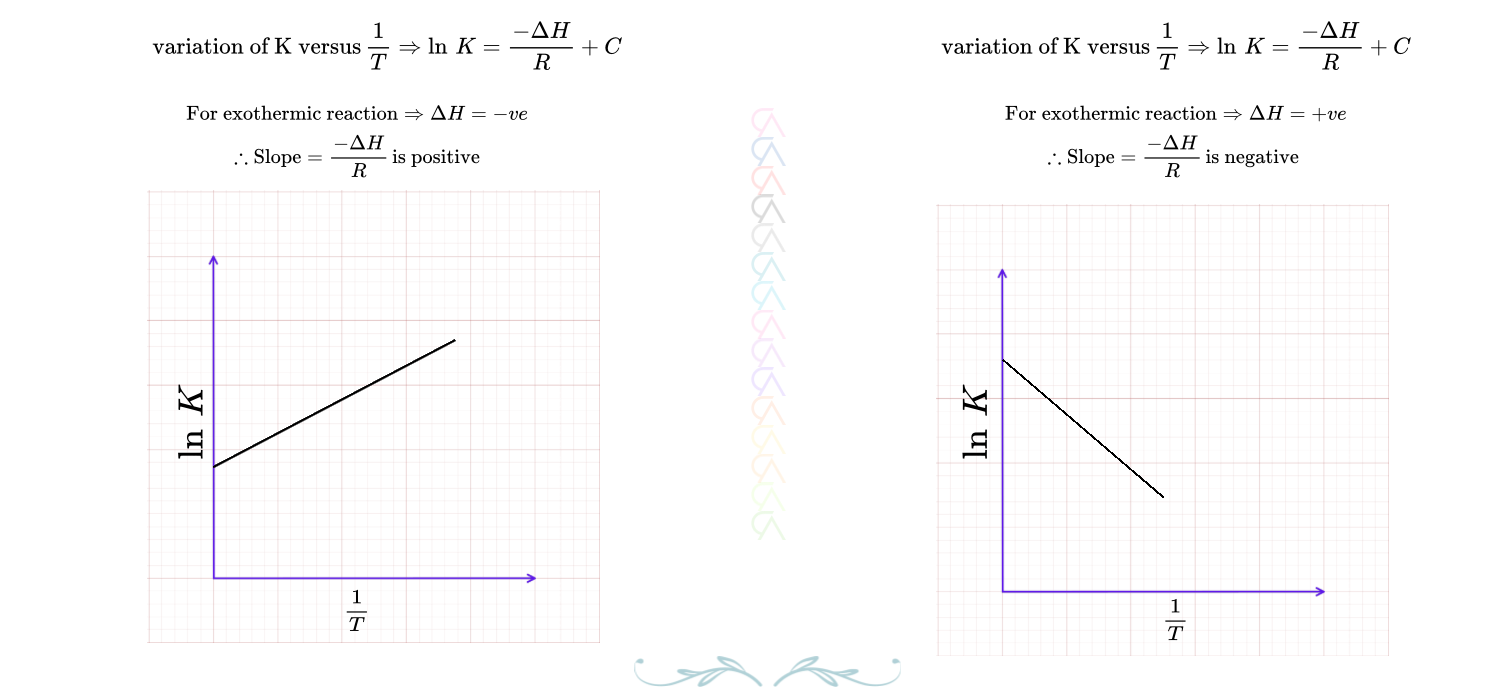
Relation between K_c and Temperature
Equilibrium constant and temperature are related and also depends on the nature of equilibrium, exothermic or endothermic.